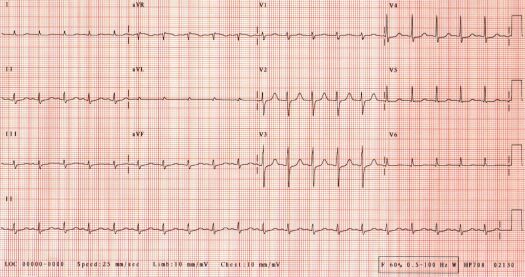
Electrocardiogram of a 19 year old lad found at home unconscious with seizure activity. Given Lorazepam i.v., intubated, transported to the Emergency Room.
Rate 173/min
PR 010 sec
QRS 010 sec
QT 0.28 sec
QTc 0.47 sec
QRS axis -
Interpretation: Abnormal. Reversed upper limb leads. Extreme sinus tachycardia.
Tall, peaked, symmetrical T waves with a narrow base suggestive of hyperkalemia.
Toxicology screen revealed cocaine toxicity. Intractable seizures required induced paralysis. The patient developed rhabdomyolysis, plasma potassium elevated to 7.2 mm/l controlled pharmacologically. Multi-organ failure subsequently included acute renal failure, myocardial infarction and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
P waves superimposed on the preceding T waves, apparent at the rate below 150/min. P wave amplitude decrease with increasing plasma K. Tall, peaked, symmetrical T waves with a narrow base, the so-called "tented" T waves, are the earliest ECG abnormality of hyperkalemia appearing at a plasma level of 5.7 mm/l.
ECG has normalized after correction of hyperkalemia - plasma potassium 3.9 mm/l.
<< back to ECG Decoder